The Environmental Impact of Electric Cars
Electric cars have quickly become a sustainable alternative to traditional gasoline-powered vehicles. As their adoption grows, many people are curious about their environmental impact. Are electric cars truly better for the planet? In this article, we’ll explore how EVs affect the environment and why they’re an essential part of the green future.
1. Introduction: Electric Cars and Environmental Concerns
The shift toward electric vehicles (EVs) is transforming the automotive industry. This change is driven by the need to reduce carbon emissions and pollution. With rising global temperatures and environmental degradation, it is clear that we need cleaner transportation options. Electric cars, powered by electricity instead of gasoline, are seen as a solution to these issues.
Key Environmental Benefits of Electric Cars:
- Zero Emissions: Electric cars have no tailpipe emissions.
- Lower Carbon Footprint: They produce fewer greenhouse gases than conventional cars.
2. Reducing Carbon Emissions with EVs
One of the biggest advantages of electric cars is their ability to reduce carbon emissions. Traditional vehicles rely on internal combustion engines, which burn gasoline or diesel and release carbon dioxide (CO2). On the other hand, electric cars only emit CO2 during the manufacturing process, making them a cleaner option for consumers.
a. Zero Tailpipe Emissions
Electric cars produce zero tailpipe emissions. This drastically reduces the amount of harmful pollutants like carbon dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter in the air.
- Cleaner Air: EVs help improve air quality in urban areas, where pollution levels tend to be highest.
- Health Benefits: Reducing pollution can lead to fewer respiratory and heart diseases.
b. Energy Source Matters
While EVs produce no emissions during operation, their total environmental impact depends on the source of the electricity used to charge them. If charged using renewable energy like solar or wind power, their carbon footprint is significantly reduced.
- Renewable Energy Integration: Charging EVs with clean energy maximizes their environmental benefits.
- Fossil Fuels vs. Clean Energy: If EVs are charged with electricity from fossil fuels, their benefits are less pronounced.
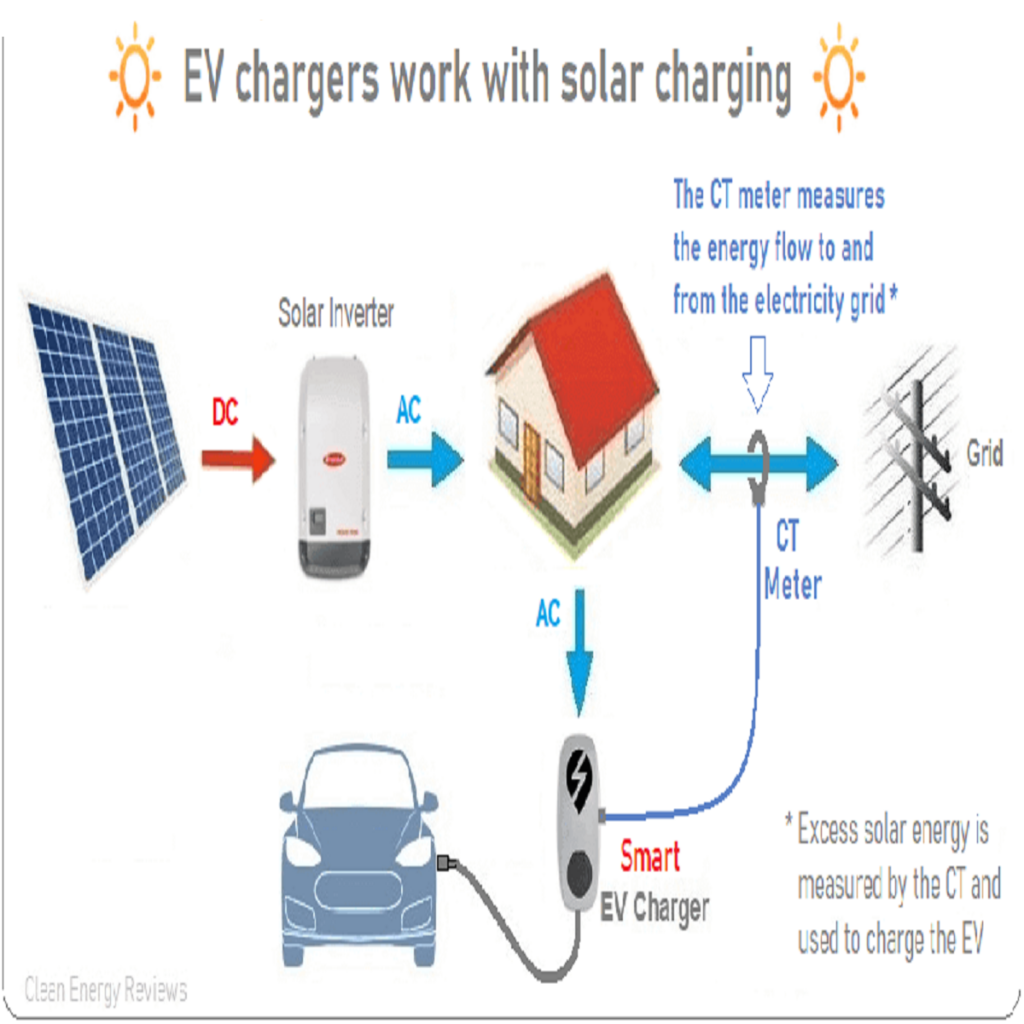
3. How EVs Reduce Air Pollution
Electric cars have a major role in reducing air pollution. Traditional cars emit large amounts of toxic gases, which contribute to smog and climate change. EVs, however, do not produce these harmful emissions, making them much cleaner for the environment.
a. Lower Greenhouse Gas Emissions
EVs help reduce overall greenhouse gas emissions. While their production may generate some emissions, studies show that over their entire lifecycle, they are still cleaner than gasoline cars.
- Long-Term Benefits: Over time, the net emissions from EVs are much lower, especially as battery production improves and renewable energy usage increases.
b. Impact on Cities
Cities often suffer from high levels of air pollution due to dense traffic and high vehicle numbers. Electric vehicles can drastically reduce the pollution levels in urban areas.
- Electric Bus Fleets: Cities are replacing diesel buses with electric models, further reducing emissions.
- Cleaner, Greener Cities: With fewer gas-powered vehicles, cities can see better air quality and improved public health.
4. Battery Production and Recycling Challenges
While EVs offer clear environmental benefits, their production does have some drawbacks. A major challenge is the environmental impact of manufacturing lithium-ion batteries. Mining raw materials such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel can cause environmental damage and social concerns.
a. Environmental Impact of Mining
Mining materials for EV batteries can result in habitat destruction and water pollution. Additionally, mining operations consume significant amounts of energy.
- Sustainable Mining Practices: Automakers are now focusing on reducing the impact of mining by adopting ethical sourcing and using more sustainable practices.
- Battery Alternatives: Research into alternative battery materials that are less damaging is ongoing.
b. Battery Recycling
As the number of electric vehicles grows, the need for effective battery recycling will also increase. Properly recycling batteries reduces the need for new materials and helps reduce the overall environmental impact.
- Repurposing Batteries: Used EV batteries can be repurposed for energy storage, reducing waste.
- Better Recycling Methods: Advances in battery recycling techniques can make EVs even more eco-friendly.
5. The Future of Electric Cars and Sustainability
The environmental impact of electric cars is expected to improve as technology advances. The future looks promising, with innovations in battery technology, cleaner manufacturing processes, and a shift to greener energy sources.
a. Improved Battery Technology
Battery technology is rapidly evolving. New innovations, like solid-state batteries, are expected to make EVs even more energy-efficient and environmentally friendly.
- Longer Battery Life: These new batteries will last longer, reducing the need for replacements.
- Less Resource-Intensive: Solid-state batteries require fewer raw materials, making them more sustainable.
b. Transition to Clean Energy
As the global energy grid transitions to renewable sources, electric cars will become even more sustainable. Charging EVs with clean energy will continue to reduce their carbon footprint.
- Global Clean Energy Movement: The ongoing push for renewable energy worldwide will ensure that EVs remain a key part of the solution to climate change.
6. Conclusion: EVs and a Greener Future
Electric cars provide significant environmental benefits, from reducing carbon emissions to improving air quality. While challenges exist, particularly in battery production and recycling, the long-term environmental impact of EVs is still far lower than that of traditional gasoline-powered vehicles. As technology advances and more clean energy sources are adopted, electric cars will continue to play an essential role in building a sustainable future for transportation.

